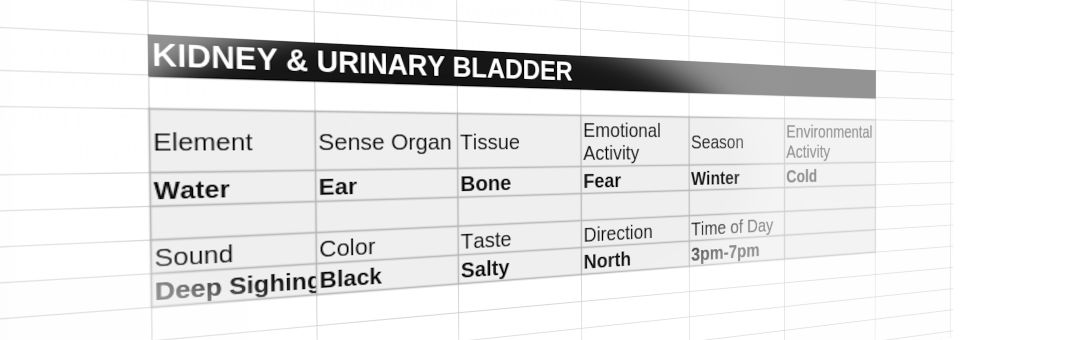
Channel Introduction: KD & UB
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) emphasizes the balance and interdependence of organ systems. The Kidney (KD) and Urinary Bladder (UB) form one of the six paired organ systems, each playing a crucial role in water metabolism, essence storage, and foundational life energy. This article introduces the KD and UB channels, their pathways, and their significance in TCM diagnosis and treatment.
The Kidney (KD) Channel
The Kidney is often referred to as the "Root of Life" in TCM. It governs birth, growth, reproduction, and development, while also supporting the body's Yin and Yang balance. The KD channel begins beneath the little toe, ascends the inner leg, and runs through the spine, connecting with the Kidney and Urinary Bladder. It further rises to the chest, throat, and tongue.
Functions of the Kidney in TCM:
- Stores Essence (Jing): The foundation of growth, reproduction, and aging.
- Governs Water Metabolism: Controls body fluids and their movement.
- Supports the Lower Back & Knees: Vitality and strength in these areas are linked to Kidney Qi.
- Houses Willpower (Zhi): Determines mental fortitude and resilience.
Common KD Pathologies:
- Kidney Yang Deficiency: Cold limbs, fatigue, weak lower back.
- Kidney Yin Deficiency: Night sweats, dry mouth, tinnitus.
- Kidney Qi Deficiency: Frequent urination, incontinence, weak knees.
The Urinary Bladder (UB) Channel
The Urinary Bladder is responsible for storing and excreting fluids. In TCM, its function extends beyond fluid management to include a crucial role in the circulation of Wei Qi (defensive energy) and the regulation of the autonomic nervous system.
The UB channel is the longest meridian, beginning at the inner corner of the eye, traveling over the head, down the back (along the paraspinal muscles), and ending at the little toe. It is often utilized in acupuncture and bodywork to influence multiple organ systems through its vast network of points.
Functions of the Urinary Bladder in TCM:
- Transforms & Excretes Fluids: Works with the Kidney to manage water balance.
- Regulates Wei Qi: Helps in defense against external pathogens.
- Influences the Nervous System: Affects the autonomic system through its pathway along the spine.
Common UB Pathologies:
- Damp-Heat in UB: Urinary discomfort, burning, urgency.
- UB Qi Deficiency: Frequent urination, leakage, low energy.
- UB Cold: Urinary retention, sensation of cold in the lower abdomen.
The KD-UB Pair: Yin & Yang Relationship
The Kidney (Yin) and Urinary Bladder (Yang) work together to regulate water metabolism and maintain the body's internal balance. The Kidney provides foundational warmth and essence, while the Urinary Bladder ensures the smooth elimination of fluids. When disharmony occurs between them, issues such as edema, urinary dysfunction, or lower back pain may arise.
Key Acupuncture Points
- KD 3 (Tai Xi): Strengthens Kidney Yin and Yang, supports lower back.
- KD 6 (Zhao Hai): Nourishes Kidney Yin, benefits the throat.
- UB 23 (Shen Shu): Tonifies the Kidney, reinforces essence.
- UB 40 (Wei Zhong): Benefits the lower back, clears heat.
Conclusion
The KD-UB channel system is fundamental in TCM, influencing not only physical health but also mental and emotional stability. By understanding their functions, pathologies, and key acupuncture points, practitioners can enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness. Strengthening this meridian pair ensures longevity, vitality, and resilience against illness, reinforcing the foundational principles of balance in TCM.
